Define Variable Step
The Define Variable step lets you create a new variable in your automation. You can give it a name, pick its data type, and set an initial value. This step is important for holding and managing data your robot uses when it runs.
How to Use the Define Variable Step
Use this step to make a new variable in your process.
Step 1: Add the Define Variable Step
- Drag the Define Variable step into your workflow.
- Click on the step to open its settings.
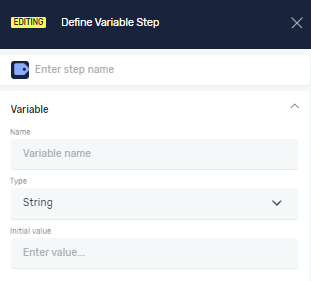
Step 2: Configure Step Information
Step Name (Optional)
- A custom name for this step in your process. This helps you find it easily in the editor.
Step 3: Set Input Parameters
Name (Required)
- Give your variable a custom name.
- Important: Variable names must follow specific rules. See the Variable Naming Rules section below.
Type (Required)
- Pick a data type from the list. This decides what kind of data the variable can hold.
- Integer: Whole numbers (e.g., 10, -5, 0).
- Decimal: Numbers with parts after the decimal point (e.g., 3.14, -0.5).
- Boolean: A true or false value.
- String: A series of characters, including text, numbers, and spaces (e.g., "Hello World", "123 Main St").
- DateTime: Stores date and/or time values.
Initial value (Optional)
- Set a starting value for your variable.
- For Integer and Decimal types, you need to provide an initial value.
- For Boolean, String, and DateTime types, an initial value is optional.
Variable Naming Rules
Follow these rules when naming your variables:
Start Character
- The variable name must begin with a letter (a-z, A-Z) or an underscore (_).
- It cannot start with a number or any other character.
Allowed Characters
- Variable names can only contain letters, numbers (0-9), and underscores (_).
- Do not use spaces, hyphens (-), special characters (like @, !, #), or punctuation.
Keyword Restriction
- The variable name cannot be a reserved keyword in Python or C#. Using a keyword will cause errors.
Disallowed Python Keywords: False, None, True, and, as, assert, async, await, break, class, continue, def, del, elif, else, except, finally, for, from, global, if, import, in, is, lambda, nonlocal, not, or, pass, raise, return, try, while, with, yield
Disallowed C# Keywords: abstract, base, bool, byte, case, catch, char, checked, const, decimal, default, delegate, do, double, enum, event, explicit, extern, fixed, float, foreach, goto, implicit, int, interface, internal, lock, long, namespace, new, null, object, operator, out, override, params, private, protected, public, readonly, ref, sbyte, sealed, short, sizeof, stackalloc, static, string, struct, switch, this, throw, typeof, uint, ulong, unchecked, unsafe, ushort, using, virtual, void, volatile
Related Articles
- Set Variable Value Step - Robotiq.ai
- Global variables - Robotiq.ai
- Set Global Variable Step - Robotiq.ai
- Switch Step - Robotiq.ai
Need Help?
Can't find what you're looking for? Join the Robotiq Community to get help from other users and the Robotiq team.
Additional comments
There are specific rules for naming variables, including keywords in C# and Python that are not allowed.
Start Character:
- The variable name must start with a letter (a-z or A-Z) or an underscore (_).
- It cannot start with a number or any other character.
Allowed Characters:
- The variable name can only contain letters, digits (0-9), and underscores (_).
- It cannot contain spaces, hyphens (-), special characters (like @, !, #, etc.), or punctuation.
Keyword Restriction:
- The name cannot be a reserved keyword in Python or C#.
- Using a keyword as a variable name would cause syntax errors or unexpected behavior.
- Disallowed: Reserved Keywords (these keywords cannot be used as variable names):
- Python keywords: False, None, True, and, as, assert, async, await, break, class, continue, def, del, elif, else, except, finally, for, from, global, if, import, in, is, lambda, nonlocal, not, or, pass, raise, return, try, while, with, yield
- C# keywords: abstract, base, bool, byte, case, catch, char, checked, const, decimal, default, delegate, do, double, enum, event, explicit, extern, fixed, float, foreach, goto, implicit, int, interface, internal, lock, long, namespace, new, null, object, operator, out, override, params, private, protected, public, readonly, ref, sbyte, sealed, short, sizeof, stackalloc, static, string, struct, switch, this, throw, typeof, uint, ulong, unchecked, unsafe, ushort, using, virtual, void, volatile
