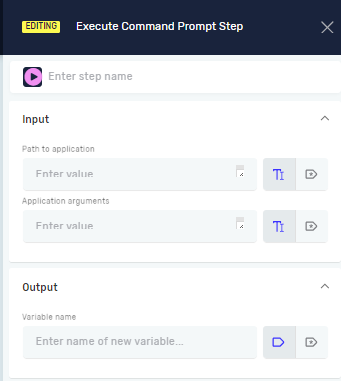
Execute Command Prompt Step
The Execute Command Prompt step runs specific commands in the Windows Command Prompt (CMD). You can use it to automate tasks that need command-line execution, like running scripts or system tools.
How to Use Execute Command Prompt
This step lets you run CMD commands or applications right from your Robotiq.ai process.
Step 1: Add the Execute Command Prompt Step
- Drag and drop the Execute Command Prompt step into your process flow.
- (Optional) In the Step name field, give the step a custom name. This helps you find it in the Process Editor.
Step 2: Set up the Command or Application
- In the Path to application field, type the full path to an executable file (for example,
C:\Windows\System32\ping.exe) or a CMD command (for example,dir C:\).- You can use a variable you already have or a direct value.
- (Optional) In the Application arguments field, add any arguments for the application or command.
- For example, if your application path is
ping.exe, the argument could begoogle.com.
- For example, if your application path is
Step 3: Get the Output
- In the Variable name field, type the name of an existing variable or make a new one.
- This variable will hold what the command puts out.
- If the command gives back a value (like
echo Hello), the variable will have that value. - If the command doesn't give back a value (like
mkdir new_folder), the variable will be empty.
- If the command gives back a value (like
Important: This step can't start an application window that other steps in your process need to refer to. Use the Open Window Process Step for that.
Parameters Explained
Step name (Optional)
- A custom name for the step in the Process Editor.
Path to application (Required)
- The full path to the
.exefile or the CMD command you want to run. - Example:
C:\Windows\System32\ipconfig.exeorping google.com
Application arguments (Optional)
- Extra settings for the application or command you put in "Path to application."
- Example: If "Path to application" is
C:\Program Files\MyTool\tool.exe, "Application arguments" could be--config myconfig.txt.
Variable name (Required)
- The name of the variable that will hold the command's output.
- You can make a new variable or use one you already have. See Define Variable Step for more information.
Related Articles
- Open Window Process Step - Learn how to open and work with application windows.
- Set Variable Value Step - Learn how to handle variable values in your processes.
Need Help?
Can't find what you're looking for? Join the Robotiq Community to get help from other users and the Robotiq team.