Select From Data Table Variable Step
The Select From Data Table Variable step runs SQL queries on variables set up as a Datatable. This step helps you filter, join, and change data inside your automation. The query result saves into a new Datatable variable.
What You'll Need
- A Datatable variable that holds data. This data can come from:
- Database queries
- Web tables (using Selenium steps)
- Excel sheets
How to Use Select From Data Table Variable
Use this step to query and change data stored in a Datatable variable.
Step 1: Add the Step to Your Process
- Drag the Select From Data Table Variable step into your process workflow.
- (Optional) Type a Step name to label the step in the editor.
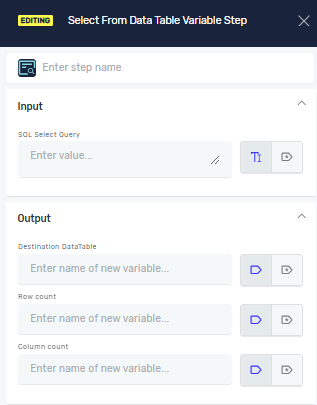
Step 2: Configure Input Parameters
- In the SQL Select Query field, type your SQL SELECT statement.
- This query runs on your Datatable variable.
- The Datatable variable's name works as the table name in your query.
- Datatable column names work as column names in your query.
Example: If you have a Datatable variable named movies with columns Id, name, and duration:
| Id | name | duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Terminator | 120 |
| 2 | Commandos | 90 |
To select all data: SELECT * FROM movies
To filter data: SELECT * FROM movies WHERE id = '1'
To join data: If you also have a Datatable variable named actors with columns Id, movie_id, and actor:
| Id | movie_id | actor |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Linda |
| 2 | 1 | Arnold |
| 3 | 2 | Arnold |
You can join these tables: SELECT actor, name AS movie_name FROM movies m JOIN actors a ON m.id = a.movie_id
Important: Use backticks () around table or column names if they have spaces or uppercase letters. For example:SELECT Titles FROM my movies WHERE id = 5`.
Step 3: Configure Output Parameters
- In the Destination DataTable field, pick an existing Datatable variable. The query result will save here.
- In the Row Count field, pick an existing or new Integer variable. This variable will hold the number of rows in the resulting Datatable.
- In the Column Count field, pick an existing or new Integer variable. This variable will hold the number of columns in the resulting Datatable.
Parameters Explained
Step name (Optional)
- A custom name for this process step.
SQL Select Query (Required)
- The SQL SELECT statement to run on your Datatable variable.
- Example:
SELECT name, duration FROM movies WHERE duration > 100 - When to use it: To filter, sort, or combine data from one or more Datatable variables.
Destination DataTable (Required)
- The Datatable variable where the query's result will be stored.
- When to use it: To save the output of your SQL query for later use in your process.
Row Count (Required)
- An Integer variable to store the number of rows in the resulting Datatable.
- When to use it: To get a count of the rows your query returned.
Column Count (Required)
- An Integer variable to store the number of columns in the resulting Datatable.
- When to use it: To get a count of the columns in the resulting Datatable.
Additional Comments
- This step uses an in-memory SQLite database to run queries. SQLite does not force data types in tables.
- When joining columns of different types, use
CASTto make sure data matches up. For example:CAST(m.id AS INTEGER) = CAST(a.movie_id AS INTEGER). - The syntax used is SQLite syntax.
Related Articles
Need Help?
Can't find what you're looking for? Join the Robotiq Community to get help from other users and the Robotiq team.